What Is Periodontal Disease?
If you have been told you have periodontal (gum) disease, you’re not alone. Many adults in the U.S. currently have some form of the disease. Periodontal diseases range from simple gum inflammation to serious disease that results in major damage to the soft tissue and bone that support the teeth. In the worst cases, teeth are lost.
Whether your gum disease is stopped, slowed, or gets worse depends a great deal on how well you care for your teeth and gums every day, from this point forward.
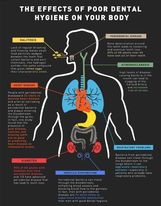
In addition to the effects on your oral health, periodontal disease can have a drastic negative impact on your overall health. Linked to Heart Disease, Respiratory Issues, Diabetes and more - this disease goes beyond your teeth and creates issues that are spread throughout your body.
Take a look at the video below, which goes over periodontal disease in further detail.
Some factors, which increase your risk for Peridontal Disease include:
- Smoking. Need another reason to quit smoking? Smoking is one of the most significant risk factors associated with the development of gum disease. Additionally, smoking can lower the chances for successful treatment.
- Hormonal changes in girls/women. These changes can make gums more sensitive and make it easier for gingivitis to develop.
- Diabetes. People with diabetes are at higher risk for developing infections, including gum disease.
- Other illnesses. Diseases like cancer or AIDS and their treatments can also negatively affect the health of gums.
- Medications. There are hundreds of prescription and over the counter medications that can reduce the flow of saliva, which has a protective effect on the mouth. Without enough saliva, the mouth is vulnerable to infections such as gum disease. And some medicines can cause abnormal overgrowth of the gum tissue; this can make it difficult to keep teeth and gums clean.
- Genetic susceptibility. Some people are more prone to severe gum disease than others
Perio Therapy: Scaling and Root Planing
|
Post Operative Instructions for Perio Therapy |
How Does My Dentist Treat Gum Disease?
Your dentist and hygienist will work closely together to help treat and reduce the signs of periodontal disease. There are various ways to treat gum disease, including:
- Deep Cleaning, often called Perio Therapy or Scaling and Root Planing
- Medications placed directly onto the affected area can help prevent the disease from getting worse, and if used in conjunction with the deep cleaning therapies can often have positive results.
- Surgical Treatments
- Flap Surgery. Surgery might be necessary if inflammation and deep pockets remain following treatment with deep cleaning and medications. A dentist or periodontist may perform flap surgery to remove tartar deposits in deep pockets or to reduce the periodontal pocket and make it easier for the patient, dentist, and hygienist to keep the area clean. This common surgery involves lifting back the gums and removing the tartar. The gums are then sutured back in place so that the tissue fits snugly around the tooth again. After surgery the gums will heal and fit more tightly around the tooth. This sometimes results in the teeth appearing longer.
- Bone and Tissue Grafts. In addition to flap surgery, your periodontist or dentist may suggest procedures to help regenerate any bone or gum tissue lost to periodontitis. Bone grafting, in which natural or synthetic bone is placed in the area of bone loss, can help promote bone growth. A technique that can be used with bone grafting is called guided tissue regeneration. In this procedure, a small piece of mesh-like material is inserted between the bone and gum tissue. This keeps the gum tissue from growing into the area where the bone should be, allowing the bone and connective tissue to regrow. Growth factors – proteins that can help your body naturally regrow bone – may also be used. In cases where gum tissue has been lost, your dentist or periodontist may suggest a soft tissue graft, in which synthetic material or tissue taken from another area of your mouth is used to cover exposed tooth roots. Since each case is different, it is not possible to predict with certainty which grafts will be successful over the long-term. Treatment results depend on many things, including how far the disease has progressed, how well the patient keeps up with oral care at home, and certain risk factors, such as smoking, which may lower the chances of success. Ask your periodontist what the level of success might be in your particular case